In early March, the GSMA announced the winners of the 2022 Global Mobile (GLOMO) Awards at the MWC Barcelona trade show. The GLOMO Awards are considered a prestigious honor for companies in the mobile industry. This year (2022), the biggest winner is Samsung, which took home the CTO Choice: Outstanding Mobile Tech Award and the Best Mobile Tech Breakthrough Award. Huawei was also recognized for winning the Best Mobile Network Infrastructure for its new FDD Giga band MIMO modules.
Also, this March, 3GPP’s Release 17 reached its third stage functional freeze. The end date (protocol freeze) for Release 17 will follow in a few months—in June 2022.
With these recent happenings, we felt that this is a good time to take a quick look at the current 5G standardization and commercialization status and examine the landscape of NG-RAN-related standard essential patents (SEPs).
Table of contents
- Standardization and commercialization status
- The NG-RAN SEP Declaration Landscape
- NG-RAN SEP owners
- The SEPs beyond just declarations
- What about essentiality?
- Findings
Standardization and commercialization status
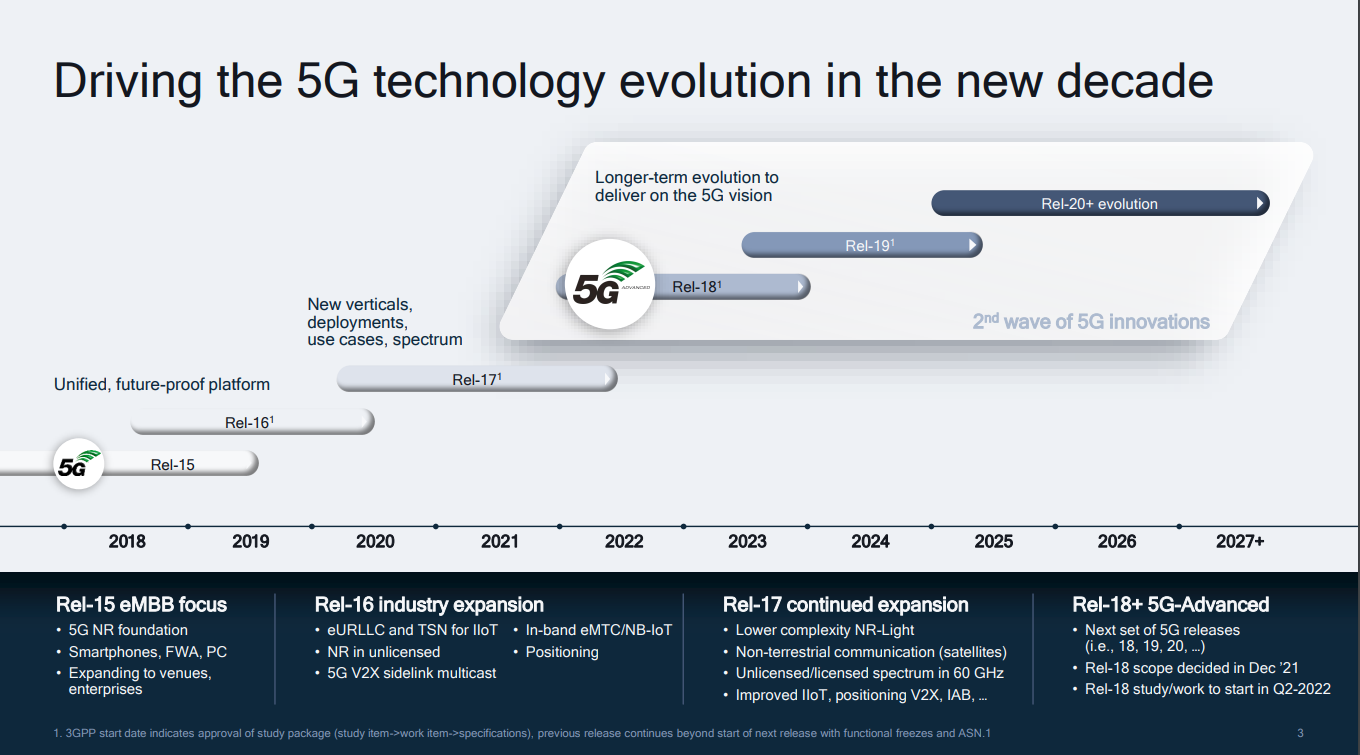
3GPP 5G Releases
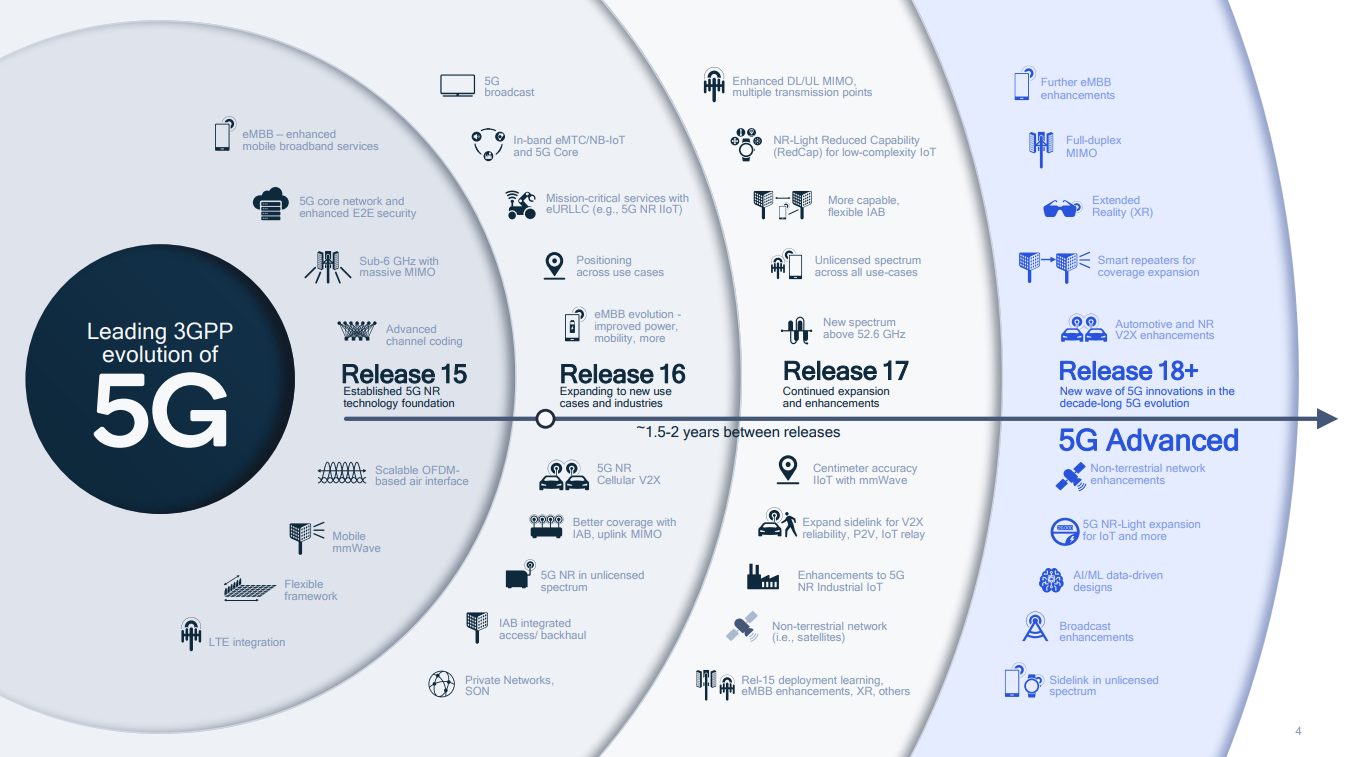
3GPP’s Releases 15, 16, and 17 have set the groundwork for the 5G, or Next-Generation (NG) radio technology, and as Release 17 nears its end date in June, we are witnessing the closure of the first wave of 5G technology innovations.
As of today, Release 15 and 16 are already frozen, and Release 17 will quickly follow. The scope and contents of Release 18, the first “5G-Advanced” release, was mostly determined in December last year (2021). However, the work for Release 18 will only officially begin after the completion of Release 17 this year.
Proposed schedule of 5G Releases
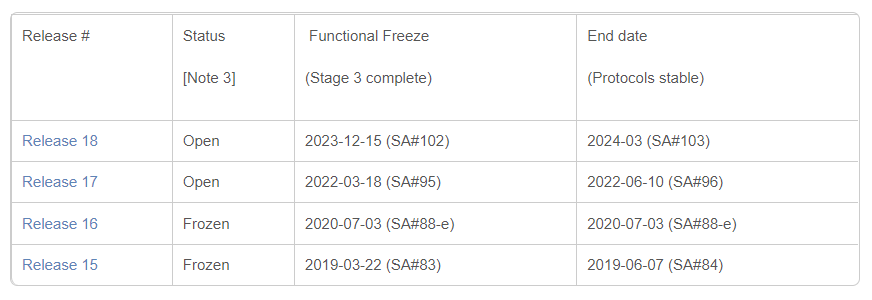
Building on NG-RAN technology, some companies are already starting to provide other proprietary functions or technologies such as open-RAN (O-RAN), virtual-RAN (v-RAN), and Cloud-RAN. What’s more, new O-RAN standards are already being developed, such as the O-RAN Alliance, founded by AT&T, China Mobile, Deutsche Telekom, NTT DOCOMO, and Orange in February of 2018.
Commercialization status
We did a little digging around to find which SEP owners are already commercializing their 5G tech and pushing their 5G RAN solutions. Five of the top SEP owners are already offering their NG-RAN solutions or products. These companies include:
Other notable SEP owners include Qualcomm and Lenovo, who are suppliers in the NG-RAN product ecosystem.
LG Electronics seems to be mainly licensing its 5G SEPs and other cellular patents to other companies after it closed down its mobile business in July 2021. Its communication service provider LG U+ has selected Ericsson as its primary 5G core network vendor.
Oppo, Xiaomi, and Vivo are mobile phone manufacturers that work with other companies such as Ericsson but have not directly commercialized their NG-RAN technology.
The NG-RAN SEP Declaration Landscape
Now let’s start looking at the rankings!
We first wanted to see the global company rankings for NG-RAN SEP declarations. In addition to using the Newly Declared, Active, and Pending filters in SEP OmniLytics, we also sifted through 3GPP technical specifications (TS) and technical reports (TR) to see which are most related to the NG-RAN technology. The TS and TR selected are based on 3GPP Release 15 and 16 features and study items that correspond to the New Radio Access technologies and 5G systems related to RAN. (Release 17 items are excluded as the Release has yet to be frozen) This article uses this list of TS/TR to find the company rankings for NG-RAN SEPs.
Here is a small excerpt from our TS/TR list:
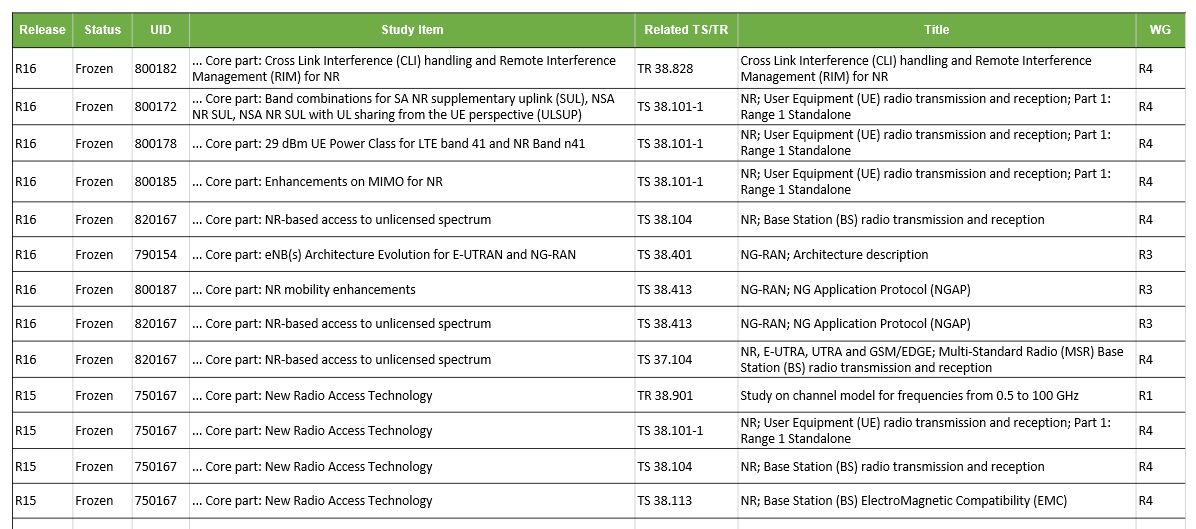
You can check out what each of SEP OmniLytics’ exclusive filters does in this SEP data article. Also, if you are interested in the list of TS/TR that are the most relevant to NG-RAN technology, contact us!
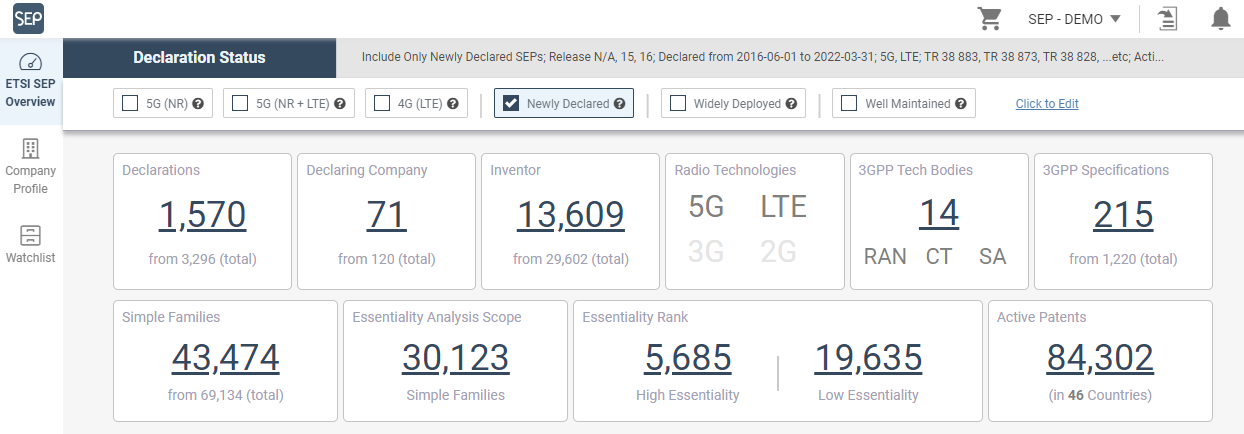
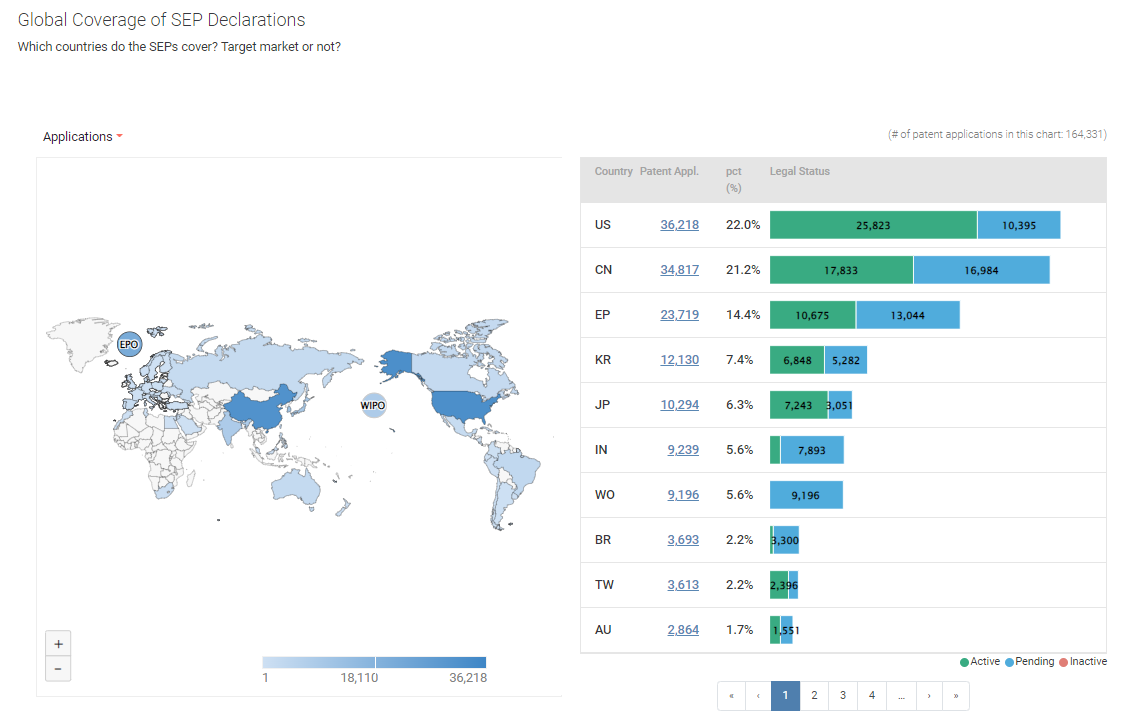
We found that a total of 71 companies have declared NG-RAN-related SEPs with ETSI and the SEPs cover 63 jurisdictions.
In Table 1, we can see the top 40 companies that have declared NG-RAN-related SEPs. The five companies that we previously identified as already commercializing their NG-RAN technology are highlighted in blue, and all rank in the top ten.

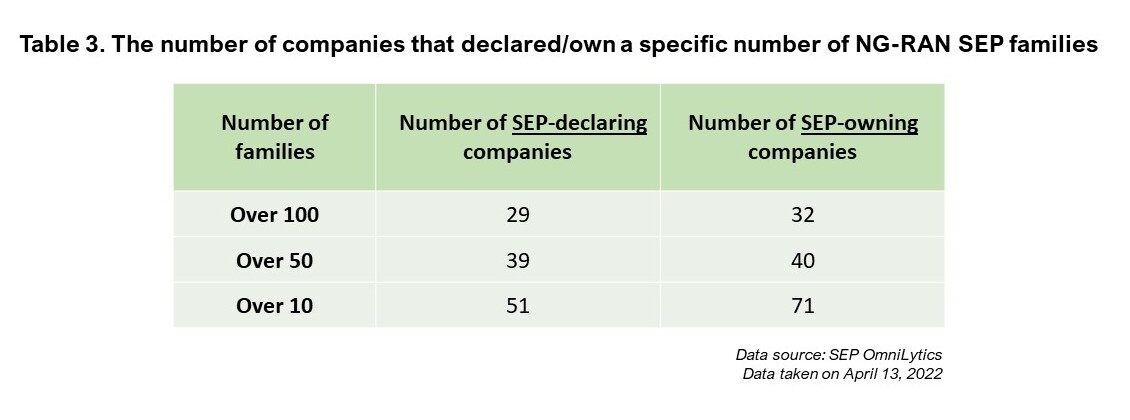
We also found that in this list, there are 51 companies that have declared more than 10 SEP families, 39 companies declared more than 50 SEP families, and 29 companies declared more than 100 families.
NG-RAN SEP owners
Now, let’s look at the ownership status of the NG-RAN SEPs. Below are the new rankings using the Current Owner tab in SEP OmniLytics.
To note, we excluded the “Newly Declared” filter from this set of criteria (and the subsequent tables in this article) to see the actual number of SEPs each company holds.
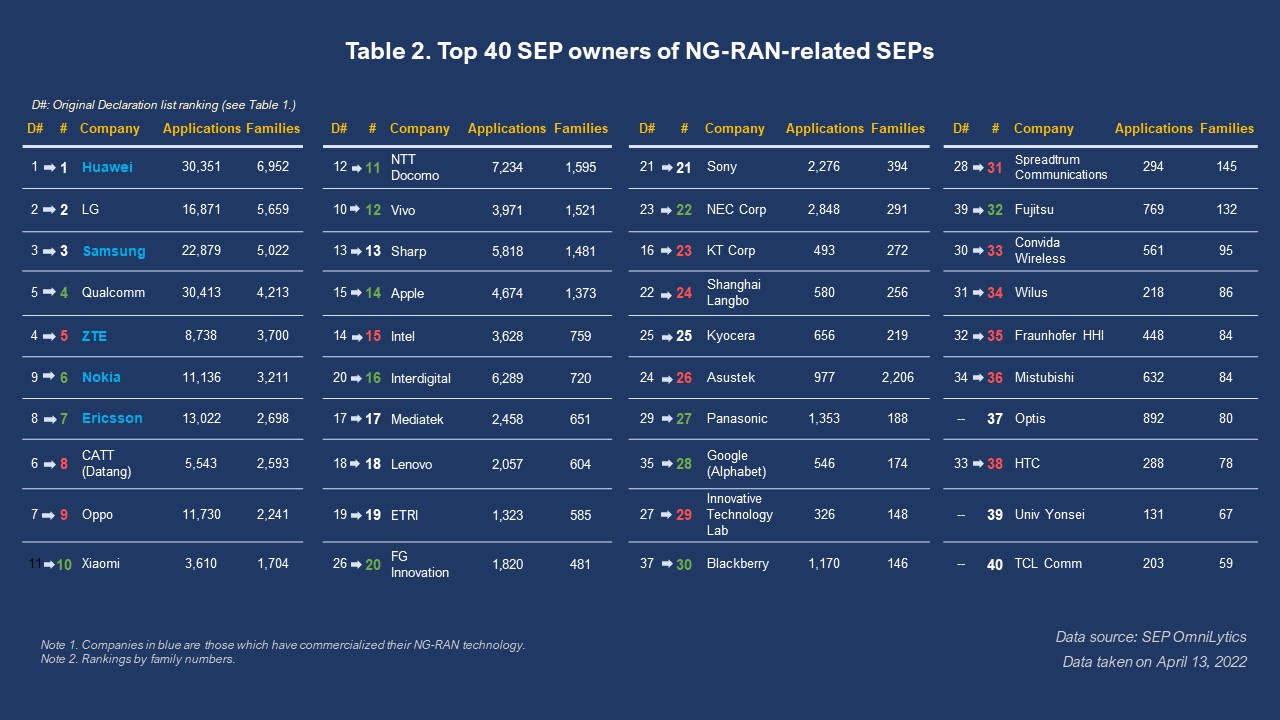
We can see that there is some, but no major reshuffling of the rankings, with instances such as Xiaomi entering the top ten and Vivo dropping to 12th place. Nearly all of the top 40 declaring companies have remained in the top 40 NG-RAN SEP-owning companies, indicating that most of the current top owners are also the declaring companies. The rankings of the top five companies remain the same as the declaring companies, and only three companies have dropped out of these rankings, namely Voiceage Corp, TCT Mobile, and Transsion. They have been replaced with Optis, Univ Yonsei, and TCL Comm.
FG Innovations shoots up six places to take the 20th place, and the number of NG-RAN SEP families it owns more than doubles the number of its declared SEPs (172 families to 481 families). We also looked at the number of SEPs with the Newly Declared filter to ensure we were not looking at SEPs previously declared. The number of SEPs FG Innovations owns is relatively the same with or without the filter (1817 applications and 480 families with the filter).
Interdigital and Blackberry also move up several places. Still, after applying the Newly Declared filter, we found that their surge in numbers is mainly attributed to the number of SEPs previously declared, unlike FG Innovations.
We can see a slight increase in the number of companies that own a specific number of NG-RAN SEP families compared to the declarations.
The SEPs beyond just declarations
Now that we know the overall positions of the NG-RAN SEP owners, let’s take a look at the SEPs that are more than merely declared.
Due to the over-declaration issue with SEPs, it is sometimes difficult to decipher the SEPs that are truly essential or even regarded as essential from those that are merely declared for the sake of adding more numbers.
The first way to sift out the SEPs that go beyond just declarations is to examine the behavioral data of the SEP-holding companies. By looking at what these companies do or do not do, we can get an overall idea of a company’s view towards its SEPs or IP policy. Simply put, we can see how a company perceives its SEPs by taking a peek at how much effort and money it is investing in its SEPs.
Let’s dig out these SEPs that go beyond mere declarations with the Well Maintained filter and the Widely Deployed filter and see who is investing the most resources!
SEPs that are Well Maintained
Well Maintained SEPs are those without any abandoned, lapsed, withdrawn, or revoked family members, indicating that their owner is investing more to keep the SEPs and their family members active. This also reflects how important a SEP is to its owner.
The results of the top 20 companies are very similar to the current owner list we just looked at in the previous section, with only some slight reshuffling of the rankings. Therefore, we have excluded the list for this section. Let us know if you are interested in the full results.
Only Interdigital drops out of the top 20, from its 16th place to 22nd, as only 35.6% (256 out of 720) of its NG-RAN SEP families are well maintained. Sony pulls up from the 21st place to fill in the gap.
The results are also quite close if we compare the overall numbers of SEP-holding companies, as we see here:
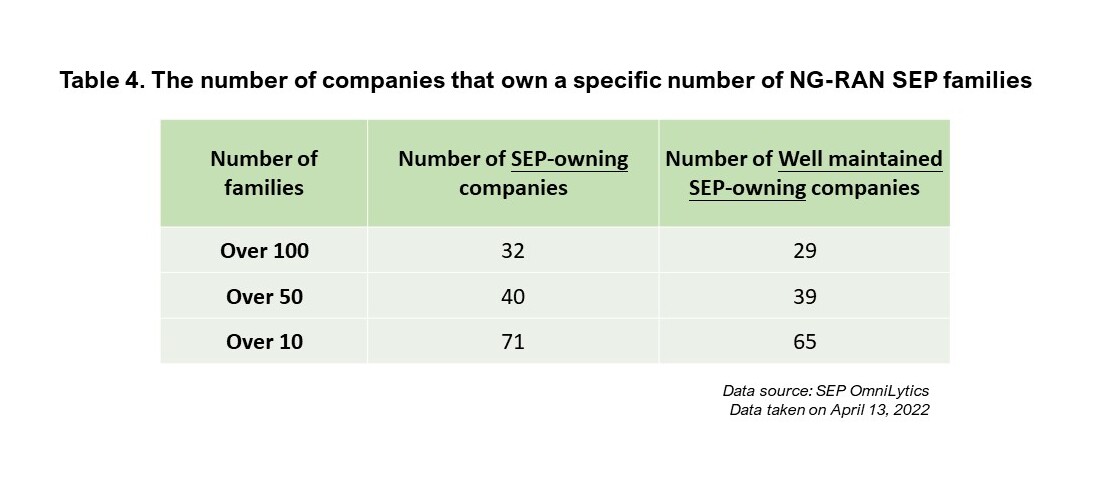
On a side note, we also discovered that the companies with the highest percentage of well-maintained NG-RAN SEPs were all Chinese companies. The top three companies are CATT (Datang), Xiaomi, and Vivo, with 93.4%, 96.4%, and 97.9%, respectively (their well-maintained rankings are #6, #10, and #11). This high percentage may suggest that Chinese companies have a more ambitious IP policy for maintaining their SEPs as there are no abandoned family members.
SEPs that are Widely Deployed around the globe
Apart from how well each SEP-holding company maintains its SEPs, we can also look at the coverage of each company’s NG-RAN SEPs to see who is more ambitious in giving their IP assets more regional coverage. We used the Widely Deployed filter to find the NG-RAN SEPs families deployed in 10 or more jurisdictions. The new rankings are as below.
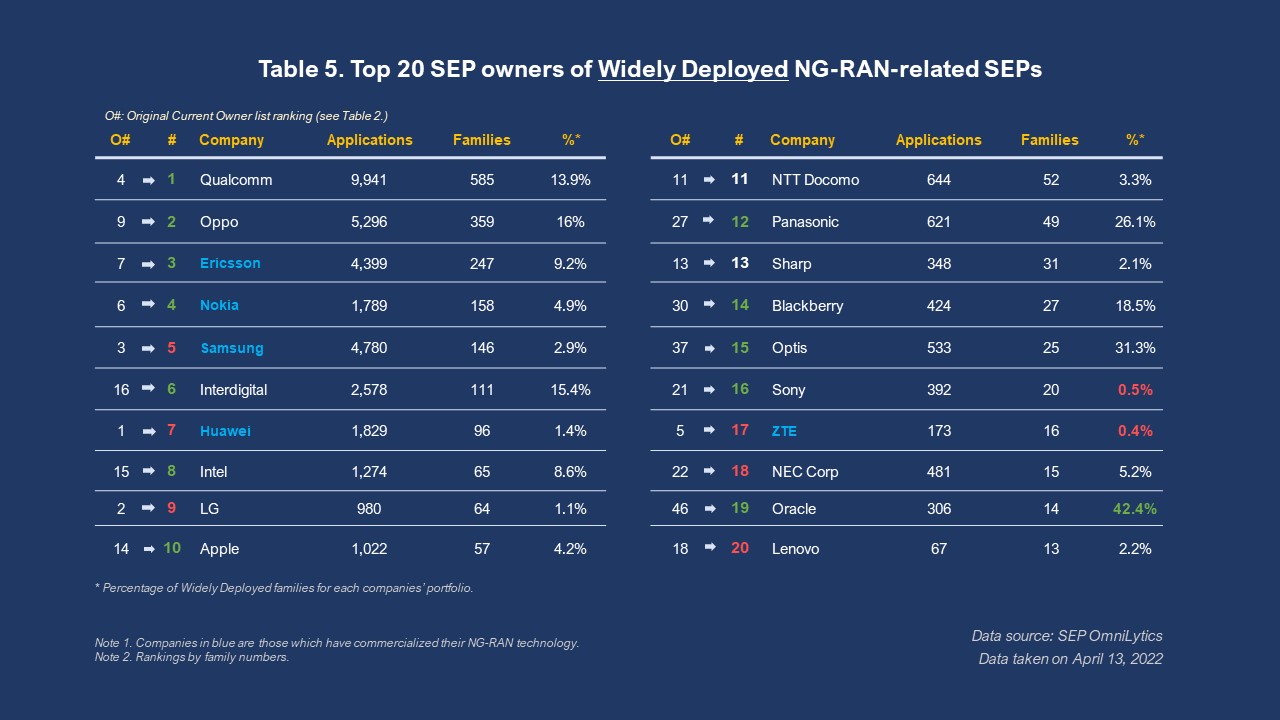
After applying this filter, the rankings showed a big reshuffling, with six companies dropping out of the top 20 and Huawei handing its crown to Qualcomm and falling to the 7th place. LG and ZTE also fall in both rankings and the percentage of widely deployed NG-RAN SEPs, especially with ZTE having only 0.54% of widely deployed SEP families.
We also see a larger drop in rankings and percentages in many Chinese companies. Meanwhile, Oppo, Interdigital, Panasonic, and Blackberry jump up higher in rankings and have higher percentages of widely deployed SEPs, especially Oppo, who took the 2nd place.
The three Chinese companies we mentioned having more well-maintained NG-RAN SEPs in the previous section, namely CATT (Datang), Xiaomi, and Vivo, are among the six companies that dropped out of the rankings. The other three companies are Mediatek, ETRI, and FG Innovation. CATT (Datang) and Mediatek dropped completely out of the entire list from their original rankings of 8th and 17th place, and the results show that these two companies have no widely-deployed NG-RAN SEP families.
When we look at the overall numbers of SEP-holding companies, the numbers drop drastically.
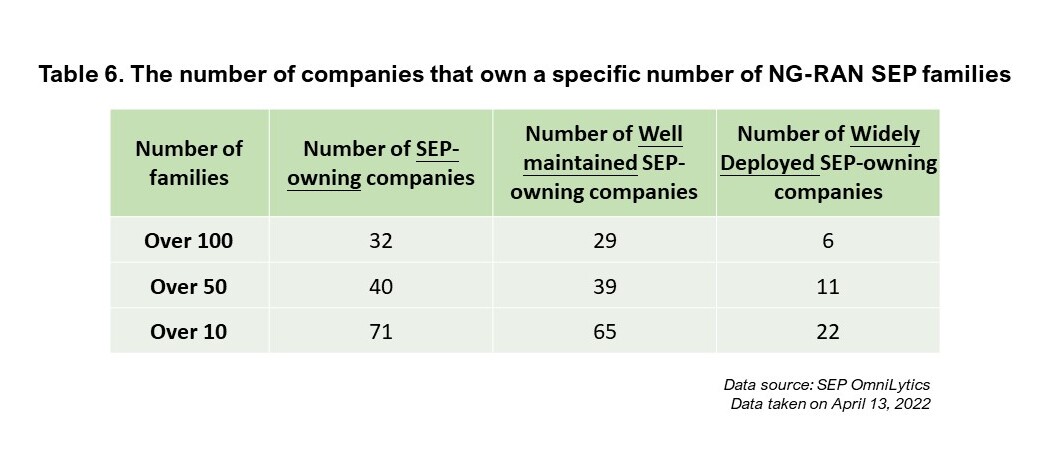
Only the top five to six companies maintain larger widely-deployed portfolios. If we exclude the essentiality factor and only look at the deployment status, this indicates that companies such as Qualcomm and Oppo will have better negotiating power when it comes to determining a regional rate for a specific country.
Quickly summarizing, we found that most of the top NG-RAN SEP-holding companies are taking good care of their NG-RAN SEPs. However, we can also see that it may be more difficult to invest in maintaining a larger portfolio and also increasing the range of its deployment at the same time.
What about essentiality?
Yes, what about essentiality?
The analysis we did in the previous section is mainly based on the self-assessment, or more specifically, the behavioral data from the SEP-holding companies. But, clearly, self-assessment data cannot give us a more objective view of the essentiality of standard essential patents, as everyone can set their own worth to their own assets.
So, we looked at the NG-RAN SEPs that rank “High” with our TS Relevancy Indicator (using the advanced filter in SEP OmniLytics).
The TS Relevancy indicator comes from mapping a SEPs claims to its declared technical specifications/reports using automated claim charts. You can read more about our exclusive essentiality indicators with our Essentiality Rankings infographic post.
Here is the claim chart of one of Oppo’s NG-RAN SEPs with high TS Relevancy as an example.
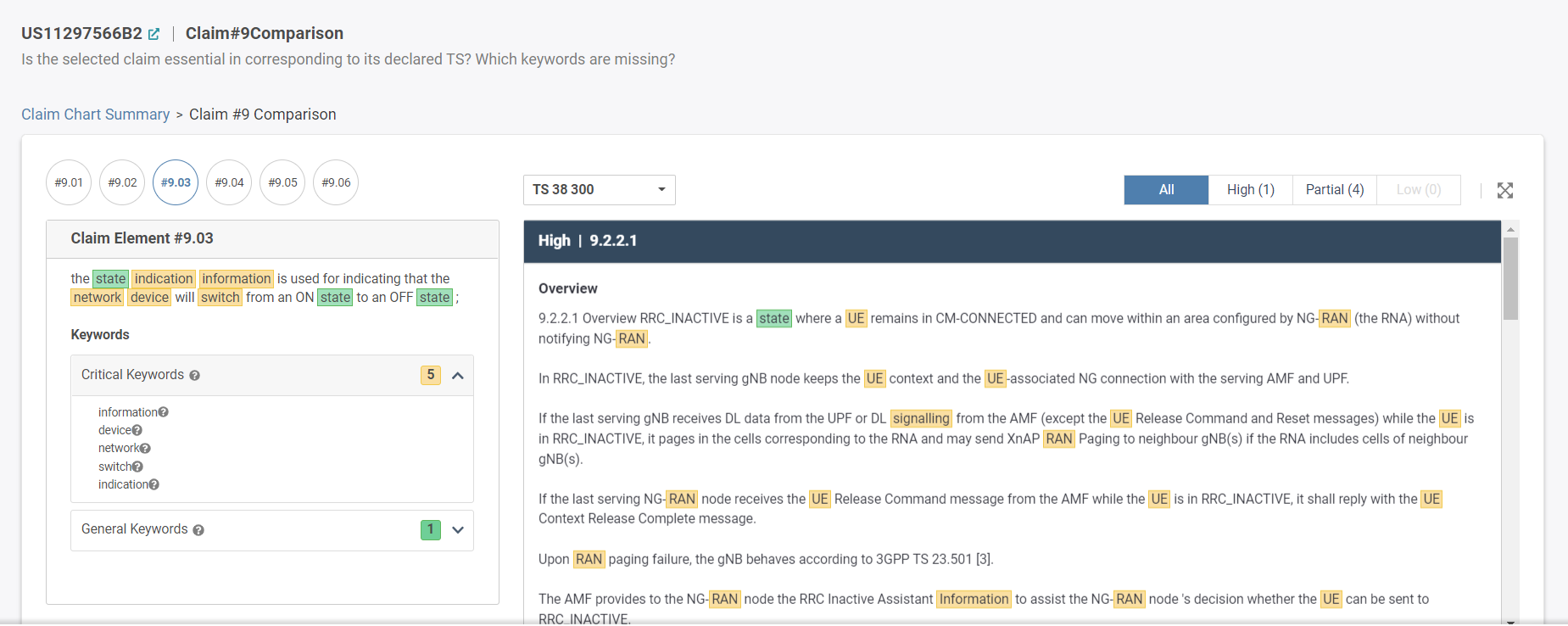
Table 7 below shows the rankings for the top 20 NG-RAN SEP-owning companies with High-TS Relevancy, indicating that their NG-RAN SEPs can be mapped to their declared TS/TR more easily.
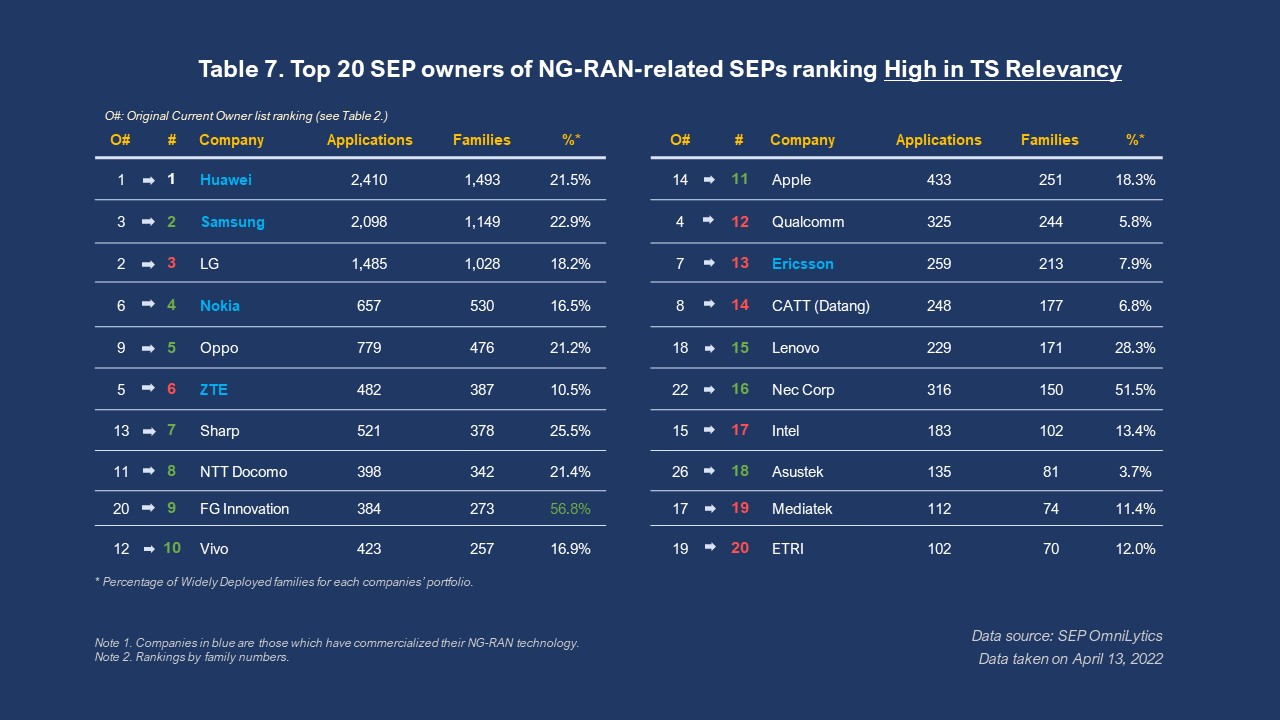
We see a slight change in the rankings, with Nokia and Oppo moving up to the top five. Qualcomm drops to 12th place from the 4th, with only 5.8% of its NG-RAN portfolio having high TS Relevancy. Xiaomi and Interdigital drop out of the list, but not far, to the 22nd and 21st place, respectively. Pushing into the top 20 are Nec Corp and Asustek, with Nec Corp having a 51.5% of high TS Relevancy NG-RAN SEPs.
Interestingly, FG Innovation has the highest percentage of high TS Relevancy NG-RAN SEPs with 56.8%, compared with the average percentage of 19.5% of the top 20 companies. Also, the average of the five NG-RAN commercialized companies is 15.8%, as Ericsson dropped to 13th place and has only 7.9% of high TS Relevancy SEPs.
Apart from the High TS Relevancy rankings, we also looked at the numbers that exclude low TS Relevancy SEPs — looking at company SEP portfolios with high and partial TS Relevancy.
The rankings for this filter are fairly similar to the original current owner list, with only a slight rearranging of the rankings. Similar to our previous findings with the high TS Relevancy filter, CATT (Datong) shows a larger drop in rankings and percentage. Our findings show that CATT’s high or partial TS relevancy NG-RAN SEPs only takes up 17.7% of its portfolio. This may be because 45.5% of CATT’s NG-RANs are deployed in China.
The average of the top 20 companies that have high or partial TS relevancy NG-RAN SEPs is 44.7%, and the average of the five companies that have commercialized their NG-RAN technology is 41.4%
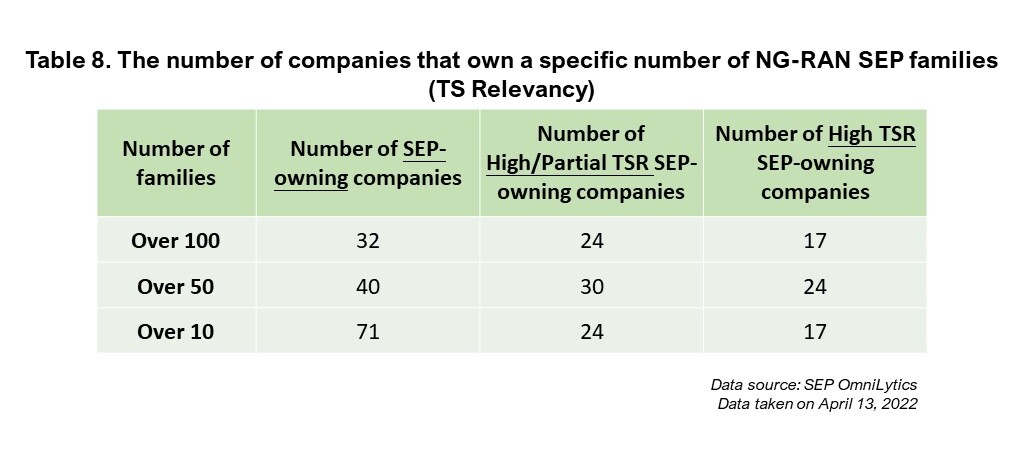
Finally, let’s take a look at the numbers of SEP-holding companies for essentiality.
Findings
After peeling away each layer of noise by examining behavioral data and analyzing the essentiality of the NG-RAN SEPs through TS/TR mapping, we found that:
- The five companies that have commercialized their NG-RAN tech are still relatively strong in terms of SEP families owned, whether through self-assessment or TS/TR mapping. Most of the commercialized companies drop in rankings only when examined under the Widely Deployed glass, especially ZTE.
- Huawei maintains the top position for most of the ranking lists due to the sheer amount of NG-RAN SEPs it holds.
- Samsung also holds a strong position, mostly in 3rd place, surpassed by LG, which does not commercialize its NG-RAN technology.
- ZTE is the fourth company in line that has commercialized its technology, taking 5th place in the current owner list, just after Qualcomm, who takes the 4th place. However, the number of ZTE’s widely deployed NG-RAN SEP families drops drastically to only 16 families, while Qualcomm takes the number 1 throne with 585 families.
- The other two companies, Nokia and Ericsson, have a sound stance in the top ten companies for most of the rankings. However, when we look at the percentage of high TS Relevancy NG-RAN SEPs, we found that Ericsson drops quite a ways to 13th place from 7th with only 7.9% of high TS Relevancy SEP families. Nokia, on the other hand, maintains a relatively stable position.
On a side note, although we have yet to hear of any commercialization of Oppo’s NG-RAN technology, it shows great potential. Always within the top ten and taking second place with widely-deployed SEPs, Oppo seems to adopt a more ambitious IP policy for NG-RAN SEPs.
With the imminent closure of the 3GPP’s first three 5G Releases this year and the commercialization of the NG-RAN technology, we are seeing more companies holding such SEPs. Although SEP OmniLytics shows that 73 companies have declared NG-RAN-related SEPs, 263 companies own such SEPs. Among these two hundred or so companies, 71 companies hold ten or more NG-RAN SEP families. This indicates that these SEP-holding companies can and may assert their SEPs in the future.
Although we looked at essentiality in this article, we didn’t delve into the quality aspect. Determining a patent’s quality is often case-by-case and requires more scrutiny and professional interpretation. If you are interested in examining the quality issues or finding potential prior art for a specific patent, you can check out our Quality Insights app.
In the meantime, you can compile your own rankings by navigating SEP OmniLytics’ automated claim charts and essentiality features today!